Our Blog
Choosing the Right Office Space: Coworking, Managed, or Conventional

Office space is no longer just a physical requirement—it is a strategic business decision that impacts cost, flexibility, company culture, and long-term scalability. From startups to large enterprises, every organization faces the same question: Should we choose coworking, opt for a managed office, or commit to a conventional leased or owned office? Each model has unique strengths, trade-offs, and hidden costs. Here’s a detailed comparison.
Coworking Offices
When to Consider
- Startups or firms entering new markets
- Businesses with uncertain headcount growth
- Companies needing immediate occupancy without capital expenditure
Advantages
- Speed of occupation with ready-to-move spaces
- Flexibility with short lock-ins and easy expansion or downsizing
- Low upfront investment as furniture, IT, and services are included
- Community environment with networking opportunities
Challenges
- Higher per-seat costs
- Limited privacy and branding opportunities
- Shared facilities may affect productivity
- Cultural alignment issues for larger enterprises
Hidden Costs: Meeting room charges, parking, storage, and premium services.
Market Trend: Large corporates now contribute 30–40% of coworking demand, using it for satellite offices, new city entries, or hybrid models.
Managed Offices
When to Consider
- Mid-to-large enterprises with stable growth for 2–5 years
- Companies needing branded private offices without upfront investment
- Organizations preferring predictable monthly costs
Advantages
- Customization in branding, layouts, and IT infrastructure
- Predictable all-inclusive costs covering rent, utilities, security, and housekeeping
- Scalability within the same operator’s ecosystem
- Enterprise-grade feel without capital expenditure
Challenges
- Higher recurring costs compared to conventional leasing
- Vendor lock-in risks
- Less economical for very long-term commitments
Hidden Costs: Charges for customization outside standard packages, lock-in and exit penalties.
Market Trend: Fastest-growing segment in India, with operators like WeWork, Awfis, Smartworks, and IndiQube serving enterprise clients of 200–2,000 seats.
Conventional Leased or Owned Offices
When to Consider
- Large, stable enterprises with long-term visibility
- Businesses prioritizing branding and complete control
- Companies viewing real estate as a long-term investment
Advantages
- Lower recurring rent per seat compared to other models
- Full control over design, branding, and vendors
- Stability through long-term leases
- Potential for asset appreciation in case of ownership
Challenges
- High upfront capital expenditure for fit-outs, deposits, and compliance
- Longer search and negotiation cycles
- Limited flexibility to downsize or exit
- Risk of underutilization if projections fall short
Hidden Costs: Maintenance charges (CAM), property taxes, compliance, and annual rental escalations of 5–8%.
Market Trend: Still the backbone for IT majors and Fortune 500s, though often complemented with coworking or managed spaces for hybrid strategies.
The Decision Matrix
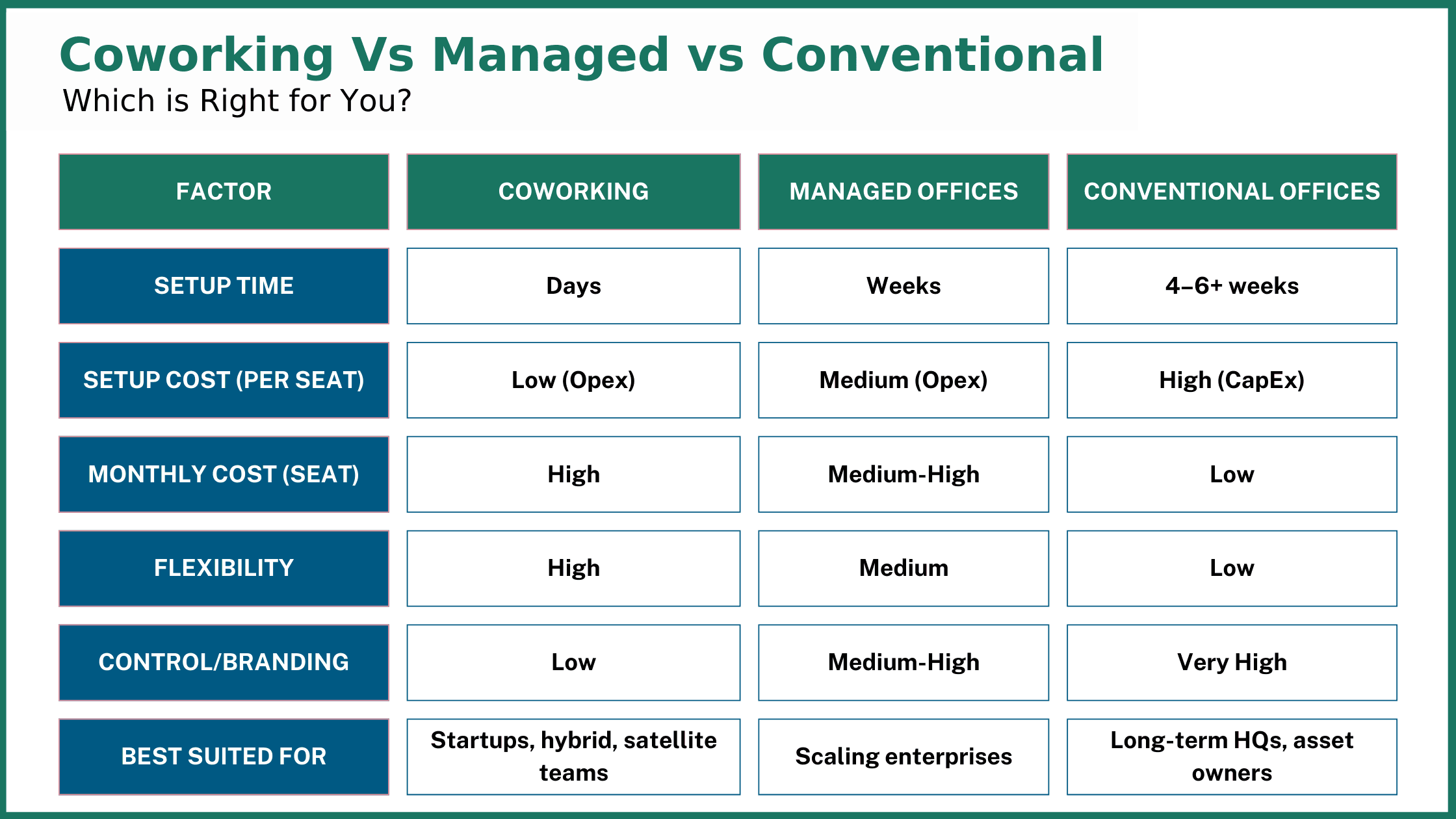
Key Insights
- Coworking offers unmatched speed and flexibility but comes at a premium.
- Managed offices strike a balance between scalability and control.
- Conventional offices provide cost efficiency and stability but lack agility.
Many enterprises today adopt a blended approach: a conventional HQ with managed or coworking setups for expansions, projects, or hybrid teams.
Aakash Jain
Director